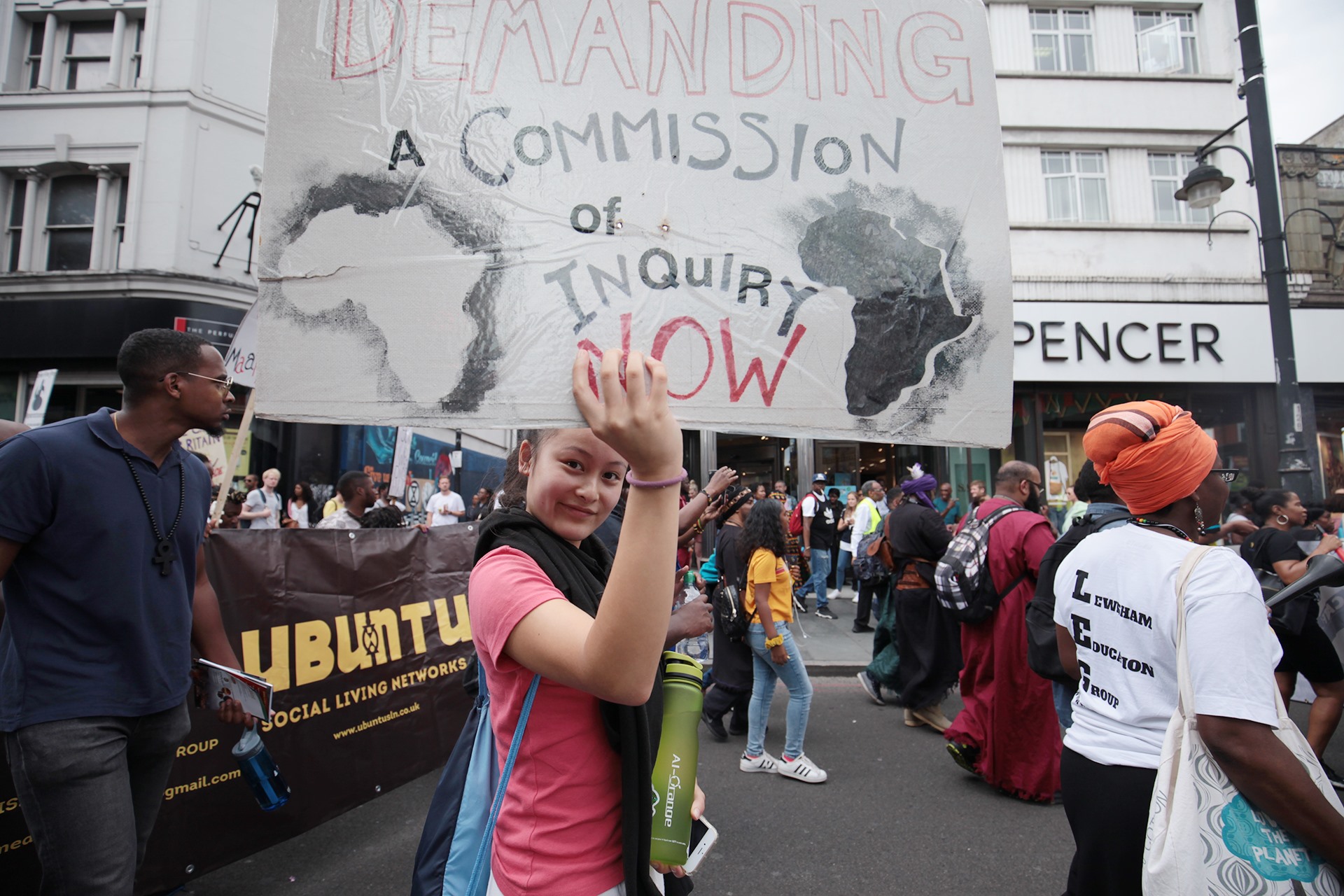The Stop The Maangamizi: We Charge Genocide/Ecocide Campaign (SMWeCGEC) has, since its inception, been campaigning for the setting up of an All-Party Parliamentary Group (APPG) to address the legacies of Afrikan Enslavement as highlighted in the Stop The Maangamizi Postcard (below). The Maangamizi is the Kiswahili term for the African Holocaust of chattel, colonial and neocolonial forms of enslavement. The call to set up an APPG on Afrikan Heritage Communities Legacies of Enslavement has now developed into a concrete proposal driven by the Maangamizi Educational Trust for the estabishment of the All-Party Parliamentary Group on African Reparations (APPGAR).
We in the SMWeCGEC have had promising discussions with various members of the British Houses of Parliament, including MPs and peers, who have agreed to set up and be part of the APPGAR. Discussions and negotiations are still taking place on a number of key issues concerninG the scope, remit and timeframe for establishing the APPGAR; nevertheless, we felt it was important to share the proposals that we have made for such an APPGAR. These proposals also include aspects of the text within the the Lambeth, Islington and Bristol ‘Atonement and Reparations‘ motions as well as text contributed by the International Network of Scholars & Activists for Afrikan Reparations (INOSAAR).

Please note in this proposal African is spelled with a C. We in the Stop The Maangamizi Campaign recognise that the consciousness raising journey of self-defining as Afrikan with a K has not begun for all people of Afrikan ancestry and heritage. Hence this starting point with a view to seeking to raise conciousness of the need for People of Afrikan heritage and ancestry to self-define as Afrikans.
DRAFT TERMS OF REFERENCE FOR THE ALL-PARTY PARLIAMENTARY GROUP ON AFRICAN REPARATIONS (APPGAR)
All-Party Parliamentary Groups (APPGs) are informal, cross-party, interest groups of MPs and Peers which meet to discuss, campaign on and promote a certain issue. Many APPGs choose to involve individuals, campaign groups, charities, and other non-governmental organisations from outside Parliament, but who are active in the field of interest, to become involved in their administration and activities. They have no official status within Parliament but can, however, be very influential in bringing matters to the attention of Parliament and ministers as well as also encouraging action by other bodies.
The All-Party Parliamentary Group on African Reparations (hereafter referred to as ‘APPGAR’) is to be established in [October] 2021 by a cross-party group of parliamentarians.
The APPGAR is to be chaired by (MP’s name withheld until agreements reached).
SHORT DESCRIPTION
The All-Party Parliamentary Group on African Reparations (APPGAR) brings together parliamentarians, campaigners, communities and other stakeholders to examine issues of African Reparations; explore policy proposals on reparations and make recommendations to Parliament on how to redress the legacies of African enslavement, colonialism and neocolonialism today.
OBJECTIVES
1. The APPGAR exists to:
(a) raise parliamentary awareness and public understanding about the meaning of, rationale, and proposals for African Reparations to address the legacies of African enslavement, colonisation and neocolonialism within and beyond the UK.
(b) study, review research and share knowledge about the effects of African enslavement, colonisation and neocolonialism within the British Empire from 1662 to the present.
(c) provide a springboard for parliamentary action on African Reparations such as debates, questions for oral and written answers and legislative reform.
(d) accelerate action on the establishment of the All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth & Reparatory Justice (APPCITARJ) and set out recommendations for the government on African Reparations proposals and measures.
(e) seek evidence on what measures and reforms are needed to address African Reparations at the level of policy.
(f) advise and make recommendations to the UK Government on African Reparations.
(g) stimulate cross-community dialogue on African Reparations and explore interconnections with reparations campaigns and movements of other Majority World Peoples.
To further the above aims the APPGAR and its members and its members will:
· Maintain an important forum for discussion of issues relevant to African Reparations, including measures to implement proposals for African Reparations such as:
(a) the establishment of the APPCITARJ;
(b) debt cancellation and repudiation;
(c) restitution of African cultural property and human remains;
(d) public disclosure about which financial institutions were involved in the enslaver compensation loan taken out by the UK Government in 1835, and restitution of the value of taxes paid by African Heritage taxpayers in Britain until 2015 to service this loan;
(e) declaring 23rd August, the United Nations ‘International Day for Remembrance of the Slave Trade and its Abolition’ as a public holiday in the UK.
· Produce high quality reports, publications and calls for action;
· Facilitate events that further the objectives of the APPGAR;
· Attend other events, meetings where influence can be brought to bear.
BACKGROUND
2. The roots of this APPGAR lie in the longstanding socio-political struggle of the International Social Movement for African Reparations (ISMAR) to have their voices heard. For centuries, African people and their descendants who were colonised and enslaved have been calling for reparatory justice to address the long-standing and harmful legacies of enslavement, colonial oppression, genocide and ecocide.
The United Kingdom establishment played a major role in the Transoceanic Traffic in Enslaved Africans (TTEA) which saw at least 15 million Africans forcibly trafficked to the Western Hemisphere with many thousands losing their lives during the crossing from Africa to the Americas on British Ships. A great deal of the wealth of the UK was founded on this vile Crime Against Humanity (CAH), and the legacies of chattel, colonial and neocolonial forms of enslavement are still prevalent in society today.
One of the most visible and enduring legacies of African enslavement, colonisation and neocolonialism is systematic Anti-Black and other forms of Afriphobic racism that exists within Western societies. The systematic racism that is ingrained in our society manifests itself in inequality in education, housing, health, employment and the criminal justice system. The legacy of African enslavement is responsible for ingraining racial inequality within Western society, that manifests itself both in overt acts of violent racism, deaths in police, prison, psychiatric custody and immigration detention in the UK, or in institutional failings to provide sufficient support and care for African Heritage Communities, such as the disproportionate impact of Covid-19 on people of African descent in the UK.
For too long, the UK Government has ignored the repercussions of Britain’s involvement in the enslavement and colonisation of African People, preferring to emphasise its role in the abolition of slavery, which led to the 1833 Slavery Abolition Act. While it is true that certain sectors and individuals within British society actively participated in, and helped to bring about, abolition of slavery in 1833, it did so only after 200 years of profiting from it. The prevalence of this historical narrative overlooks the fact that many within the British political establishment actively resisted the abolition of slavery, not least of which was Britain’s former Prime Minister William Gladstone. It was men like Gladstone who argued for the need for the enslavers to be financially compensated, resulting in the passing of the Slave Compensation Act in1837. This allowed the enslavers (rather than the enslaved) to receive a total of £20 million in compensation, amounting to 40% of the Treasury’s annual income at the time.[1]
That debt was not fully repaid by British taxpayers until 2015, allowing the bulk of the wealth of the European-led TTEA to remain in the hands of powerful elites and their institutions in both the former colonies and in the UK.
The APPGAR will also seek to build on the work done by campaigners in the UK to advance the cause of reparations.
In 1993 Bernie Grant, MP tabled Early Day Motion (EDM) #1987 in the House of Commons welcoming the Abuja Proclamation after the first Pan-African Conference on Reparations for Enslavement, Colonisation and Neocolonisation sponsored by the Organisation of African Unity urging all countries who were enriched by enslavement and colonisation to review the case for reparations for “Africa and to Africans in the Diaspora”.
In 2003 the Lambeth based Black Quest for Justice Campaign (BQJC) supported by the Pan-Afrikan Reparations Coalition in Europe (PARCOE) initiated a class action for Pan-African Reparations for Global Justice against Queen Elizabeth II and agents of the Crown as Head of State and Head of the British Commonwealth; calling for the establishment of a Reparations Commission of Inquiry. This action was denied on the grounds that the Crown could not be prosecuted, and these crimes could not be enforced prior to the enactment of the International Criminal Courts Act in 2001.
In 2004 the Rastafarian Movement were denied their appeal for reparation because the UK government felt it could not be held responsible for events of past centuries.
In 2013 Caribbean Heads of Governments established the CARICOM Reparations Commission (CRC) with a mandate to prepare the case for reparatory justice for the region’s indigenous and African descendant communities who are the victims of Crimes against Humanity in the forms of genocide, slavery, slave trading, and racial apartheid.
From 2015 to 2019, the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign in association with the Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations March Committee co-organised the annual Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations March on the 1st of August, commemorated as Emancipation Day. In 2020 the Stop The Maangamizi Campaign and the Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations March Committee evolved the tactic of marching to co-organising the Pan-Afrikan Reparations Rebellion Groundings (PARRG) annually on the 1st of August. The Stop The Maangamizi Campaign presents the Stop the Maangamizi Petition to the Office of the UK Prime Minister annually calling for the establishment of the UK All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth and Reparatory Justice (APPCITARJ).
In July 2020 Lambeth Council, home to the largest African Caribbean population in the UK, became the first local authority in the UK to pass a successful Atonement and Reparations for the Transoceanic Trafficking of Enslaved Africans motion followed by Bristol City Council in March 2021 calling for the establishment of the APPCITARJ to address the impact of African enslavement, colonisation and neocolonialism on present generations of People of African descent and their environments.
The APPCITARJ is a campaigning initiative founded by the Pan-Afrikan Reparations Coalition in Europe (PARCOE) and now driven by the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign. The need for this Commission has long been supported by the work and activism of other members of the International Social Movement for Afrikan Reparations (ISMAR), including those of the Pan-Afrikan Liberation Movement and the INOSAAR. The campaign aims to urge the UK Government to commit to a holistic process of atonement and reparations in accordance with the United Nations Framework on a Right to A Remedy and Reparations. A key part of the process includes recognizing and addressing the longstanding legacies of African enslavement, colonialism and neo-colonialism, such as Afriphobic Racism and the racial discrimination of People of African descent and other Majority World Peoples, socio-economic inequality and environmental injustice.
The APPCITARJ’s main purpose is to inform the public of the nature of African enslavement and colonialism, as well as its long-term consequences, including present-day impacts of neocolonialism upon both individuals and communities. It will kick start a political process where the space to fully bring people together and listen to the voices of those who are normally excluded would be given the opportunity to be heard. It is intended to be participatory in nature, meaning that it will call for submissions from all those with knowledge of the nature and impacts of enslavement and colonialism to provide testimony. These include, but are not limited to: individuals, organisations, academics, communities and nations.
At a practical level, it is the process of conducting this Commission that is of the utmost importance. In order to be able to hear all voices on this matter, we need a mechanism similar to but building on the ‘Commission to Study and Develop Reparation Proposals Act for African-Americans Act’, (also known as HR40) that will act as a conduit for that conversation.[2]
This process cannot be bypassed because there are so many different constituencies and Communities of African Reparations Interest that need to be heard. The APPCITARJ will provide the basis for affected communities and individuals to voice their own self-determined solutions in effecting reparatory justice, and will identify the steps needed to facilitate their participation in any reparatory process in which the UK is engaged going forwards.
SECRETARIAT
3. The secretariat for the APPGAR is provided by the Maangamizi Educational Trust (MET) with the support of the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign and the International Network of Scholars and Activists for Afrikan Reparations (INOSAAR).
The MET works in servicing the SMWeCGEC and its partners with highly qualitative community-based research, mindful of UNESCO guidelines, as well as with action learning, public conscientization, mainly through cross-community dialogue, and other lifelong learning ways and means of mural and extra-mural education; doing so in order to ensure Cognitive Justice becomes the key driving impetus in the promotion of broad societal awareness about the full meaning, creative application and practical realisation of African Reparations as a matter of total Pan-African Liberation and the ‘Maatubuntu’ emancipation of all Humanity, in furtherance of holistically transformative African Heritage Community Self-Repairs as an integral part of Planet Repairs in Global Justice meaningfulness.
The MET guides the SMWeCGEC in its public intellectual work for the organic development of unifying Peoples’ Power to support not only grassroots Community Activist campaigners engaged in Pan-African Reparatory Justice Advocacy Action Learning, but also all interested public officials, including members of Parliament, local and central government officials, teachers and students and youths at all levels, including complimentary and supplementary education in their variations. The MET seeks, by so doing, to encourage, guide and provide all other forms of support, to enable such entities to organically learn to grasp the full meaning and practical know how in all ramifications of effecting holistic African Reparations in such ways of ‘Maatubuntu’ creativity as to embrace Planet Repairs in Global Justice meaningfulness.
In this regard, the MET works in guiding the SMWeCGEC and its partners with public intellectual support for its efforts towards establishing the APPCITARJ.
In this regard, the MET provides technical and administrative support to the APPGAR, upholds the rules of APPGs, and acts as a key contact/coordinator for meetings and members.
The role of the Secretariat is to act as a designated secondary enquiry point alongside the Chair, who is the main registered contact. The Secretariat supports the Chair to ensure records are maintained according to APPG rules. The Secretariat maintains a list of active members – both parliamentary and external; dates of meeting – both past and future; minutes of past formal meetings (which will record both attendance and decisions); any reports or other publications issued; and income and expenditure statements as required. The Secretariat also acts as the conduit for contact with sponsors, supporters, any external advisory functions and individual experts who may interact with the APPGAR.
The interaction between the Secretariat and outside bodies is determined and subject to approval by the elected APPGAR officers.
Where bespoke and original research is to be carried out to uncover new insights and support the APPGAR’s decision-making, the MET will lead on carrying out this work. The MET will also manage any sponsorship monies, events and expenses, keeping full accounts records and making any necessary declarations of interest within the rules of the APPGAR.
The APPGAR has a Memorandum of Understanding with the MET which covers the role of the secretariat and gives responsibility for maintaining personal data as the Data Processor for the APPGAR in accordance with the principles and legal obligations of the UK General Data Protection Regulation (UK GDPR) and related legislation.
The APPGAR’s Privacy Statement can be downloaded here….[to be added]
Further support provided to the APPGAR secretariat will be declared when confirmed.
The Secretariat will be supported by a Parliamentary Coordinator on administrative matters, such as registration, parliamentary event organisation, meeting scheduling, minute taking, communications, but with a particular focus on supporting the Chair.
PUBLIC ENQUIRY POINT
4. Esther Stanford-Xosei, Chair of the MET. Email: maangamizitrust@gmail.com.
MEMBERS
5. MPs and members of the House of Lords from all parties are invited to join the APPGAR – if you are interested in exploring issues concerning African Reparations and other forms of transitional justice, we very much encourage you to join.
Officers of the group include: [Names withheld]
Other members of the group include: [Names witheld]
Members of the general public are encouraged to contact their local MP to encourage them to show interest in joining the APPGAR – either as a permanent member or for specific discussions – to play an active part in furthering African Reparatory Justice in the UK.
ADVISORY PANEL
6. External organisations and individuals are permitted to offer advice and contribute to the strategy of the APPGAR if the relationship is properly defined and declared and a register of interests is maintained by the group Secretariat.
An Advisory Panel will consist of independent specialists with specific expertise including policy or research expertise in all areas related to African Reparations who work in association with INOSAAR and adhere to its ‘Principles of Participation’ as a benchmark for good practice. The Advisory Panel will provide expert knowledge and guidance to the APPGAR.
The Advisory Panel of the APPGAR cannot have a formal relationship with the APPGAR – it is merely an informal function that can offer support on matters undertaken to further the objectives of the APPGAR. The officers of the APPGAR have the final say over all workstreams and strategic decisions taken by the group.
SUPPORTING ORGANISATIONS
7. Alongside its parliamentary members, the APPGAR invites Supporting Organisations with a campaigning track record or who undertake research and advocacy on African Reparations to contribute valuable opinions and expertise to work of the APPGAR.
Being a Supporting Organisation of the APPGAR does not necessarily signify support for or opposition to any particular reparations focused policy or initiative, but rather a desire to facilitate and informed, evidence-based dialogue and debate on African Reparations.
The APPGAR does not grant voting rights to Supporting Organisations. A full list of Supporting Organisations will be published in due course on the APPGAR page on the APPGAR Website.
PROGRAMME OF WORK
8. The APPGAR members will work together to build its annual programme of work. As part of its programme, the APPGAR will:
(a) hold an inquiry into the Legacies of African Enslavement on African Heritage Communities and;
(b) regularly review:
· new and emerging research on Reparations, working closely with civil society, academic as well as local, regional, national and international policy;
· Local, regional and international innovation, comparisons and best practice and the APPGAR may look to produce reports/documents following its own inquiries into specific areas. It will also signpost to and reference any external reports and information that it feels are appropriate to the topic and work of the APPGAR.
The APPGAR will ensure involvement of a broad diversity of African Heritage Communities within and beyond the UK, including people of African descent from all backgrounds in the work of the APPGAR, paying particular attention to the involvement of women and young people.
PURPOSE AND STRUCTURE OF THE INQUIRY
9. The purpose of this inquiry is, on a global level, to:
- Redress global inequalities caused by the Transoceanic Trafficking of Enslaved Africans (TTEA). These include, but are not limited to, social, economic and ecological harms;
- Acknowledge the fundamental injustice, cruelty, brutality, and inhumanity of the imposition of the Maangamizi, i.e. African chattel, colonial and neocolonial enslavement within and beyond the British Empire;
- Examine the health, social, environmental and climate impacts of neocolonialism as it impacts on African Heritage Communities;
- Examine Afriphobia and subsequent de jure and de facto racial and socio-economic discrimination against Africans and people of African descent, including their gendered impacts and consequences;
- Examine how African enslavement, colonialism and neocolonialism have directly benefited societal institutions, both public and private, including higher education and other public sector organisations, corporations, as well as religious organisations;
- Make recommendations to Parliament and similar bodies at local, national and international levels, including the European Parliament, and;
- Determine appropriate methods of dissemination of findings to the public within and beyond Britain for consultation about proposals for supporting initiatives of African Heritage Community Self-Repairs, Planet Repairs and designing other forms of redress and repairs.
Written evidence
The APPGAR is calling for evidence from organisations and individuals to be submitted to inform its recommendations to the UK Government on African Reparations proposals. All evidence received will be reviewed and submissions of particular interest may be followed up with an invitation to submit oral evidence.
This call for evidence is to get a better understanding of what reparations focused proposals and solutions are already taking place, and what needs to happen to address the legacies of African enslavement, colonisation and neocolonialism within and beyond the UK.
The inquiry would particularly welcome written evidence on the following key questions:
(a) What evidence is there to help understand the impact that enslavement, colonialism and neocolonialism have had on people of African descent and African Heritage Communities?
(b) What challenges/barriers are faced by people of African descent and African Heritage Communities in overcoming the legacies of enslavement, colonialism and neocolonialism?
(c) Are there examples of best practice in implementing reparations proposals and what lessons can be learned from other Majority World Communities experiences of implementing reparations proposals?
(d) What are the most effective measures the UK Government and other bodies could take to ensure that the crimes and violations of enslavement, colonialism and neocolonialism are repaired and redressed?
All written evidence should be emailed to:…., Coordinator of APPGAR. Any queries to that email: or telephone ….
The APPGAR will use responses to the call for evidence phase of the inquiry to inform and legislative proposals on African Reparations.
Oral evidence
The APPGAR is planning to hold a number of oral evidence sessions in February 2022 with a variety of people being invited to give their testimonies. Hearing African Heritage Communities’ stories and acknowledging the truth about their experiences is essential for healing and justice for people of African descent.
Report
A report, based on the written and oral evidence, will be produced which will make clear recommendations for the government and public policy decision makers.
MEETINGS AND EVENTS
10. The APPGAR will hold a minimum of two meetings per year, in the accordance with the rules on APPGs. Details of these meetings will be announced in due course. The APPGAR may also host a number of events throughout the year.
FINANCIALS
11. The APPGAR receives no taxpayer funding. However, funding is required to run a professional and effective group. There are costs associated with administration, event management, running a webpage and more. The APPGAR is currently seeking funding to support both its secretarial work for members, and for specific projects. External organisations and individuals are invited to sponsor the APPGAR to help pay for secretariat services to manage trips, events, research, the websites and reports produced by the APPGAR.
For example, if a report or other publication has been compiled or funded by any external organisation or individual, this will be made clear on the front cover of the report using the wording provided by the APPG Registrar’s office. The APPGAR is also required to identify sources of external funding on its headed paper. If the APPGAR receives over £12,500 from outside Parliament, in money or in kind, in its reporting year, it will undertake the reporting and declarations set out in the official rule book. All funds received (no matter how great or small the amount) are declared; and all monies go directly to funding salaries and reasonable expenses of the APPGAR Secretariat; nothing goes, or will ever go, to any officer or Parliamentarian.
A List of Supporters is maintained by the Secretariat and published externally along with the names of sponsors. Supporters are invited to attend all public meetings and may be invited to give evidence as or when appropriate.
Any monies received relating to the APPGAR will be declared on the UK Parliament website within 28 days of receipt. All funds received (no matter how great or small the amount) are declared in the Register of All-Party Groups, which is compiled and published by the Office of the Parliamentary Commissioner for Standards.
Sponsors have no say over the running of the APPGAR, and sponsorship confers no special access or privileges.
It is the role of the Officers of the APPGAR to ensure transparency and independence within the group.
Full year accounts will be prepared by the MET and made available upon request
Please reach out to ……..if you would like to discuss options for providing funding, large or small.
GUIDELINES FOR COMMUNICATION
12. Sponsors and partners can communicate their association with the APPGAR. Once the reporting rules for declaring a financial or professional contribution are complied with, sponsors and partners are free to communicate their association with the group and the APPGAR can do the same. That includes sponsors and partners being able to take pictures and promote their involvement with the APPGAR on social media.
The following provides high-level principles for sponsors, supporting organisations and partners to follow when communicating their involvement externally:
• Press releases or statements announcing sponsorship/partnership should be signed off by the APPGAR Secretariat.
• Sponsors can acknowledge their affiliation with the APPGAR as a sponsor, but cannot use the APPGAR logo for their own PR and marketing purposes.
The APPGAR logo is only for use on the APPGAR’s letterhead, reports, website, and social media accounts such as Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
• Tweets and other social media posts confirming an organisation is a sponsor, supporting organisation or partner and proud to support the aims of the group are appropriate but committing the APPGAR to policy positions outside the scope of the group’s aims and objectives are not appropriate unless the Secretariat has approved it
• Announcing support or funding for publications or events should be approved by the APPGAR Secretariat.
• APPGAR policy positions are agreed by the officers and Parliamentarians of the group. Sponsors, supporting organisations and partners should consider posting social media comments that complement the work and views of the APPGAR.
• APPGAR Advisory Panel meetings are internal meetings so discretion is needed on what constitutes appropriate promotion by sponsors and partners and should be approved by the APPGAR Secretariat.
[1] Kris Manjapra, ‘When will Britain face up to its crimes against humanity,’ The Guardian, 29 March 2018,https://www.theguardian.com/news/2018/mar/29/slavery-abolition-compensation-when-will-britain-face-up-to-its-crimes-against-humanity.
[2] ‘H.R. 3745 Commission to Study Reparation Proposal for African Americans Act,’ 101st Congress (1989–1990), 20 November 1989, https://www.congress.gov/bill/101st-congress/house-bill/3745. Having been submitted by congressman John Conyers Jr every year since 1989, the House Judiciary Committee held a hearing to consider reparations for the descendants of African Americans who had been enslaved on 19 June 2019.