


The Stop The Maangamizi: We Charge Genocide/Ecocide Campaign (SMWeCGEC) has, since its inception, been campaigning for the setting up of an All-Party Parliamentary Group (APPG) to address the legacies of Afrikan Enslavement as highlighted in the Stop The Maangamizi Postcard (below). The Maangamizi is the Kiswahili term for the African Holocaust of chattel, colonial and neocolonial forms of enslavement. The call to set up an APPG on Afrikan Heritage Communities Legacies of Enslavement has now developed into a concrete proposal driven by the Maangamizi Educational Trust for the estabishment of the All-Party Parliamentary Group on African Reparations (APPGAR).
We in the SMWeCGEC have had promising discussions with various members of the British Houses of Parliament, including MPs and peers, who have agreed to set up and be part of the APPGAR. Discussions and negotiations are still taking place on a number of key issues concerninG the scope, remit and timeframe for establishing the APPGAR; nevertheless, we felt it was important to share the proposals that we have made for such an APPGAR. These proposals also include aspects of the text within the the Lambeth, Islington and Bristol ‘Atonement and Reparations‘ motions as well as text contributed by the International Network of Scholars & Activists for Afrikan Reparations (INOSAAR).

Please note in this proposal African is spelled with a C. We in the Stop The Maangamizi Campaign recognise that the consciousness raising journey of self-defining as Afrikan with a K has not begun for all people of Afrikan ancestry and heritage. Hence this starting point with a view to seeking to raise conciousness of the need for People of Afrikan heritage and ancestry to self-define as Afrikans.
DRAFT TERMS OF REFERENCE FOR THE ALL-PARTY PARLIAMENTARY GROUP ON AFRICAN REPARATIONS (APPGAR)
All-Party Parliamentary Groups (APPGs) are informal, cross-party, interest groups of MPs and Peers which meet to discuss, campaign on and promote a certain issue. Many APPGs choose to involve individuals, campaign groups, charities, and other non-governmental organisations from outside Parliament, but who are active in the field of interest, to become involved in their administration and activities. They have no official status within Parliament but can, however, be very influential in bringing matters to the attention of Parliament and ministers as well as also encouraging action by other bodies.
The All-Party Parliamentary Group on African Reparations (hereafter referred to as ‘APPGAR’) is to be established in [October] 2021 by a cross-party group of parliamentarians.
The APPGAR is to be chaired by (MP’s name withheld until agreements reached).
SHORT DESCRIPTION
The All-Party Parliamentary Group on African Reparations (APPGAR) brings together parliamentarians, campaigners, communities and other stakeholders to examine issues of African Reparations; explore policy proposals on reparations and make recommendations to Parliament on how to redress the legacies of African enslavement, colonialism and neocolonialism today.
OBJECTIVES
1. The APPGAR exists to:
(a) raise parliamentary awareness and public understanding about the meaning of, rationale, and proposals for African Reparations to address the legacies of African enslavement, colonisation and neocolonialism within and beyond the UK.
(b) study, review research and share knowledge about the effects of African enslavement, colonisation and neocolonialism within the British Empire from 1662 to the present.
(c) provide a springboard for parliamentary action on African Reparations such as debates, questions for oral and written answers and legislative reform.
(d) accelerate action on the establishment of the All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth & Reparatory Justice (APPCITARJ) and set out recommendations for the government on African Reparations proposals and measures.
(e) seek evidence on what measures and reforms are needed to address African Reparations at the level of policy.
(f) advise and make recommendations to the UK Government on African Reparations.
(g) stimulate cross-community dialogue on African Reparations and explore interconnections with reparations campaigns and movements of other Majority World Peoples.
To further the above aims the APPGAR and its members and its members will:
· Maintain an important forum for discussion of issues relevant to African Reparations, including measures to implement proposals for African Reparations such as:
(a) the establishment of the APPCITARJ;
(b) debt cancellation and repudiation;
(c) restitution of African cultural property and human remains;
(d) public disclosure about which financial institutions were involved in the enslaver compensation loan taken out by the UK Government in 1835, and restitution of the value of taxes paid by African Heritage taxpayers in Britain until 2015 to service this loan;
(e) declaring 23rd August, the United Nations ‘International Day for Remembrance of the Slave Trade and its Abolition’ as a public holiday in the UK.
· Produce high quality reports, publications and calls for action;
· Facilitate events that further the objectives of the APPGAR;
· Attend other events, meetings where influence can be brought to bear.
BACKGROUND
2. The roots of this APPGAR lie in the longstanding socio-political struggle of the International Social Movement for African Reparations (ISMAR) to have their voices heard. For centuries, African people and their descendants who were colonised and enslaved have been calling for reparatory justice to address the long-standing and harmful legacies of enslavement, colonial oppression, genocide and ecocide.
The United Kingdom establishment played a major role in the Transoceanic Traffic in Enslaved Africans (TTEA) which saw at least 15 million Africans forcibly trafficked to the Western Hemisphere with many thousands losing their lives during the crossing from Africa to the Americas on British Ships. A great deal of the wealth of the UK was founded on this vile Crime Against Humanity (CAH), and the legacies of chattel, colonial and neocolonial forms of enslavement are still prevalent in society today.
One of the most visible and enduring legacies of African enslavement, colonisation and neocolonialism is systematic Anti-Black and other forms of Afriphobic racism that exists within Western societies. The systematic racism that is ingrained in our society manifests itself in inequality in education, housing, health, employment and the criminal justice system. The legacy of African enslavement is responsible for ingraining racial inequality within Western society, that manifests itself both in overt acts of violent racism, deaths in police, prison, psychiatric custody and immigration detention in the UK, or in institutional failings to provide sufficient support and care for African Heritage Communities, such as the disproportionate impact of Covid-19 on people of African descent in the UK.
For too long, the UK Government has ignored the repercussions of Britain’s involvement in the enslavement and colonisation of African People, preferring to emphasise its role in the abolition of slavery, which led to the 1833 Slavery Abolition Act. While it is true that certain sectors and individuals within British society actively participated in, and helped to bring about, abolition of slavery in 1833, it did so only after 200 years of profiting from it. The prevalence of this historical narrative overlooks the fact that many within the British political establishment actively resisted the abolition of slavery, not least of which was Britain’s former Prime Minister William Gladstone. It was men like Gladstone who argued for the need for the enslavers to be financially compensated, resulting in the passing of the Slave Compensation Act in1837. This allowed the enslavers (rather than the enslaved) to receive a total of £20 million in compensation, amounting to 40% of the Treasury’s annual income at the time.[1]
That debt was not fully repaid by British taxpayers until 2015, allowing the bulk of the wealth of the European-led TTEA to remain in the hands of powerful elites and their institutions in both the former colonies and in the UK.
The APPGAR will also seek to build on the work done by campaigners in the UK to advance the cause of reparations.
In 1993 Bernie Grant, MP tabled Early Day Motion (EDM) #1987 in the House of Commons welcoming the Abuja Proclamation after the first Pan-African Conference on Reparations for Enslavement, Colonisation and Neocolonisation sponsored by the Organisation of African Unity urging all countries who were enriched by enslavement and colonisation to review the case for reparations for “Africa and to Africans in the Diaspora”.
In 2003 the Lambeth based Black Quest for Justice Campaign (BQJC) supported by the Pan-Afrikan Reparations Coalition in Europe (PARCOE) initiated a class action for Pan-African Reparations for Global Justice against Queen Elizabeth II and agents of the Crown as Head of State and Head of the British Commonwealth; calling for the establishment of a Reparations Commission of Inquiry. This action was denied on the grounds that the Crown could not be prosecuted, and these crimes could not be enforced prior to the enactment of the International Criminal Courts Act in 2001.
In 2004 the Rastafarian Movement were denied their appeal for reparation because the UK government felt it could not be held responsible for events of past centuries.
In 2013 Caribbean Heads of Governments established the CARICOM Reparations Commission (CRC) with a mandate to prepare the case for reparatory justice for the region’s indigenous and African descendant communities who are the victims of Crimes against Humanity in the forms of genocide, slavery, slave trading, and racial apartheid.
From 2015 to 2019, the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign in association with the Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations March Committee co-organised the annual Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations March on the 1st of August, commemorated as Emancipation Day. In 2020 the Stop The Maangamizi Campaign and the Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations March Committee evolved the tactic of marching to co-organising the Pan-Afrikan Reparations Rebellion Groundings (PARRG) annually on the 1st of August. The Stop The Maangamizi Campaign presents the Stop the Maangamizi Petition to the Office of the UK Prime Minister annually calling for the establishment of the UK All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth and Reparatory Justice (APPCITARJ).
In July 2020 Lambeth Council, home to the largest African Caribbean population in the UK, became the first local authority in the UK to pass a successful Atonement and Reparations for the Transoceanic Trafficking of Enslaved Africans motion followed by Bristol City Council in March 2021 calling for the establishment of the APPCITARJ to address the impact of African enslavement, colonisation and neocolonialism on present generations of People of African descent and their environments.
The APPCITARJ is a campaigning initiative founded by the Pan-Afrikan Reparations Coalition in Europe (PARCOE) and now driven by the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign. The need for this Commission has long been supported by the work and activism of other members of the International Social Movement for Afrikan Reparations (ISMAR), including those of the Pan-Afrikan Liberation Movement and the INOSAAR. The campaign aims to urge the UK Government to commit to a holistic process of atonement and reparations in accordance with the United Nations Framework on a Right to A Remedy and Reparations. A key part of the process includes recognizing and addressing the longstanding legacies of African enslavement, colonialism and neo-colonialism, such as Afriphobic Racism and the racial discrimination of People of African descent and other Majority World Peoples, socio-economic inequality and environmental injustice.
The APPCITARJ’s main purpose is to inform the public of the nature of African enslavement and colonialism, as well as its long-term consequences, including present-day impacts of neocolonialism upon both individuals and communities. It will kick start a political process where the space to fully bring people together and listen to the voices of those who are normally excluded would be given the opportunity to be heard. It is intended to be participatory in nature, meaning that it will call for submissions from all those with knowledge of the nature and impacts of enslavement and colonialism to provide testimony. These include, but are not limited to: individuals, organisations, academics, communities and nations.
At a practical level, it is the process of conducting this Commission that is of the utmost importance. In order to be able to hear all voices on this matter, we need a mechanism similar to but building on the ‘Commission to Study and Develop Reparation Proposals Act for African-Americans Act’, (also known as HR40) that will act as a conduit for that conversation.[2]
This process cannot be bypassed because there are so many different constituencies and Communities of African Reparations Interest that need to be heard. The APPCITARJ will provide the basis for affected communities and individuals to voice their own self-determined solutions in effecting reparatory justice, and will identify the steps needed to facilitate their participation in any reparatory process in which the UK is engaged going forwards.
SECRETARIAT
3. The secretariat for the APPGAR is provided by the Maangamizi Educational Trust (MET) with the support of the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign and the International Network of Scholars and Activists for Afrikan Reparations (INOSAAR).
The MET works in servicing the SMWeCGEC and its partners with highly qualitative community-based research, mindful of UNESCO guidelines, as well as with action learning, public conscientization, mainly through cross-community dialogue, and other lifelong learning ways and means of mural and extra-mural education; doing so in order to ensure Cognitive Justice becomes the key driving impetus in the promotion of broad societal awareness about the full meaning, creative application and practical realisation of African Reparations as a matter of total Pan-African Liberation and the ‘Maatubuntu’ emancipation of all Humanity, in furtherance of holistically transformative African Heritage Community Self-Repairs as an integral part of Planet Repairs in Global Justice meaningfulness.
The MET guides the SMWeCGEC in its public intellectual work for the organic development of unifying Peoples’ Power to support not only grassroots Community Activist campaigners engaged in Pan-African Reparatory Justice Advocacy Action Learning, but also all interested public officials, including members of Parliament, local and central government officials, teachers and students and youths at all levels, including complimentary and supplementary education in their variations. The MET seeks, by so doing, to encourage, guide and provide all other forms of support, to enable such entities to organically learn to grasp the full meaning and practical know how in all ramifications of effecting holistic African Reparations in such ways of ‘Maatubuntu’ creativity as to embrace Planet Repairs in Global Justice meaningfulness.
In this regard, the MET works in guiding the SMWeCGEC and its partners with public intellectual support for its efforts towards establishing the APPCITARJ.
In this regard, the MET provides technical and administrative support to the APPGAR, upholds the rules of APPGs, and acts as a key contact/coordinator for meetings and members.
The role of the Secretariat is to act as a designated secondary enquiry point alongside the Chair, who is the main registered contact. The Secretariat supports the Chair to ensure records are maintained according to APPG rules. The Secretariat maintains a list of active members – both parliamentary and external; dates of meeting – both past and future; minutes of past formal meetings (which will record both attendance and decisions); any reports or other publications issued; and income and expenditure statements as required. The Secretariat also acts as the conduit for contact with sponsors, supporters, any external advisory functions and individual experts who may interact with the APPGAR.
The interaction between the Secretariat and outside bodies is determined and subject to approval by the elected APPGAR officers.
Where bespoke and original research is to be carried out to uncover new insights and support the APPGAR’s decision-making, the MET will lead on carrying out this work. The MET will also manage any sponsorship monies, events and expenses, keeping full accounts records and making any necessary declarations of interest within the rules of the APPGAR.
The APPGAR has a Memorandum of Understanding with the MET which covers the role of the secretariat and gives responsibility for maintaining personal data as the Data Processor for the APPGAR in accordance with the principles and legal obligations of the UK General Data Protection Regulation (UK GDPR) and related legislation.
The APPGAR’s Privacy Statement can be downloaded here….[to be added]
Further support provided to the APPGAR secretariat will be declared when confirmed.
The Secretariat will be supported by a Parliamentary Coordinator on administrative matters, such as registration, parliamentary event organisation, meeting scheduling, minute taking, communications, but with a particular focus on supporting the Chair.
PUBLIC ENQUIRY POINT
4. Esther Stanford-Xosei, Chair of the MET. Email: maangamizitrust@gmail.com.
MEMBERS
5. MPs and members of the House of Lords from all parties are invited to join the APPGAR – if you are interested in exploring issues concerning African Reparations and other forms of transitional justice, we very much encourage you to join.
Officers of the group include: [Names withheld]
Other members of the group include: [Names witheld]
Members of the general public are encouraged to contact their local MP to encourage them to show interest in joining the APPGAR – either as a permanent member or for specific discussions – to play an active part in furthering African Reparatory Justice in the UK.
ADVISORY PANEL
6. External organisations and individuals are permitted to offer advice and contribute to the strategy of the APPGAR if the relationship is properly defined and declared and a register of interests is maintained by the group Secretariat.
An Advisory Panel will consist of independent specialists with specific expertise including policy or research expertise in all areas related to African Reparations who work in association with INOSAAR and adhere to its ‘Principles of Participation’ as a benchmark for good practice. The Advisory Panel will provide expert knowledge and guidance to the APPGAR.
The Advisory Panel of the APPGAR cannot have a formal relationship with the APPGAR – it is merely an informal function that can offer support on matters undertaken to further the objectives of the APPGAR. The officers of the APPGAR have the final say over all workstreams and strategic decisions taken by the group.
SUPPORTING ORGANISATIONS
7. Alongside its parliamentary members, the APPGAR invites Supporting Organisations with a campaigning track record or who undertake research and advocacy on African Reparations to contribute valuable opinions and expertise to work of the APPGAR.
Being a Supporting Organisation of the APPGAR does not necessarily signify support for or opposition to any particular reparations focused policy or initiative, but rather a desire to facilitate and informed, evidence-based dialogue and debate on African Reparations.
The APPGAR does not grant voting rights to Supporting Organisations. A full list of Supporting Organisations will be published in due course on the APPGAR page on the APPGAR Website.
PROGRAMME OF WORK
8. The APPGAR members will work together to build its annual programme of work. As part of its programme, the APPGAR will:
(a) hold an inquiry into the Legacies of African Enslavement on African Heritage Communities and;
(b) regularly review:
· new and emerging research on Reparations, working closely with civil society, academic as well as local, regional, national and international policy;
· Local, regional and international innovation, comparisons and best practice and the APPGAR may look to produce reports/documents following its own inquiries into specific areas. It will also signpost to and reference any external reports and information that it feels are appropriate to the topic and work of the APPGAR.
The APPGAR will ensure involvement of a broad diversity of African Heritage Communities within and beyond the UK, including people of African descent from all backgrounds in the work of the APPGAR, paying particular attention to the involvement of women and young people.
PURPOSE AND STRUCTURE OF THE INQUIRY
9. The purpose of this inquiry is, on a global level, to:
Written evidence
The APPGAR is calling for evidence from organisations and individuals to be submitted to inform its recommendations to the UK Government on African Reparations proposals. All evidence received will be reviewed and submissions of particular interest may be followed up with an invitation to submit oral evidence.
This call for evidence is to get a better understanding of what reparations focused proposals and solutions are already taking place, and what needs to happen to address the legacies of African enslavement, colonisation and neocolonialism within and beyond the UK.
The inquiry would particularly welcome written evidence on the following key questions:
(a) What evidence is there to help understand the impact that enslavement, colonialism and neocolonialism have had on people of African descent and African Heritage Communities?
(b) What challenges/barriers are faced by people of African descent and African Heritage Communities in overcoming the legacies of enslavement, colonialism and neocolonialism?
(c) Are there examples of best practice in implementing reparations proposals and what lessons can be learned from other Majority World Communities experiences of implementing reparations proposals?
(d) What are the most effective measures the UK Government and other bodies could take to ensure that the crimes and violations of enslavement, colonialism and neocolonialism are repaired and redressed?
All written evidence should be emailed to:…., Coordinator of APPGAR. Any queries to that email: or telephone ….
The APPGAR will use responses to the call for evidence phase of the inquiry to inform and legislative proposals on African Reparations.
Oral evidence
The APPGAR is planning to hold a number of oral evidence sessions in February 2022 with a variety of people being invited to give their testimonies. Hearing African Heritage Communities’ stories and acknowledging the truth about their experiences is essential for healing and justice for people of African descent.
Report
A report, based on the written and oral evidence, will be produced which will make clear recommendations for the government and public policy decision makers.
MEETINGS AND EVENTS
10. The APPGAR will hold a minimum of two meetings per year, in the accordance with the rules on APPGs. Details of these meetings will be announced in due course. The APPGAR may also host a number of events throughout the year.
FINANCIALS
11. The APPGAR receives no taxpayer funding. However, funding is required to run a professional and effective group. There are costs associated with administration, event management, running a webpage and more. The APPGAR is currently seeking funding to support both its secretarial work for members, and for specific projects. External organisations and individuals are invited to sponsor the APPGAR to help pay for secretariat services to manage trips, events, research, the websites and reports produced by the APPGAR.
For example, if a report or other publication has been compiled or funded by any external organisation or individual, this will be made clear on the front cover of the report using the wording provided by the APPG Registrar’s office. The APPGAR is also required to identify sources of external funding on its headed paper. If the APPGAR receives over £12,500 from outside Parliament, in money or in kind, in its reporting year, it will undertake the reporting and declarations set out in the official rule book. All funds received (no matter how great or small the amount) are declared; and all monies go directly to funding salaries and reasonable expenses of the APPGAR Secretariat; nothing goes, or will ever go, to any officer or Parliamentarian.
A List of Supporters is maintained by the Secretariat and published externally along with the names of sponsors. Supporters are invited to attend all public meetings and may be invited to give evidence as or when appropriate.
Any monies received relating to the APPGAR will be declared on the UK Parliament website within 28 days of receipt. All funds received (no matter how great or small the amount) are declared in the Register of All-Party Groups, which is compiled and published by the Office of the Parliamentary Commissioner for Standards.
Sponsors have no say over the running of the APPGAR, and sponsorship confers no special access or privileges.
It is the role of the Officers of the APPGAR to ensure transparency and independence within the group.
Full year accounts will be prepared by the MET and made available upon request
Please reach out to ……..if you would like to discuss options for providing funding, large or small.
GUIDELINES FOR COMMUNICATION
12. Sponsors and partners can communicate their association with the APPGAR. Once the reporting rules for declaring a financial or professional contribution are complied with, sponsors and partners are free to communicate their association with the group and the APPGAR can do the same. That includes sponsors and partners being able to take pictures and promote their involvement with the APPGAR on social media.
The following provides high-level principles for sponsors, supporting organisations and partners to follow when communicating their involvement externally:
• Press releases or statements announcing sponsorship/partnership should be signed off by the APPGAR Secretariat.
• Sponsors can acknowledge their affiliation with the APPGAR as a sponsor, but cannot use the APPGAR logo for their own PR and marketing purposes.
The APPGAR logo is only for use on the APPGAR’s letterhead, reports, website, and social media accounts such as Facebook, Twitter and Instagram.
• Tweets and other social media posts confirming an organisation is a sponsor, supporting organisation or partner and proud to support the aims of the group are appropriate but committing the APPGAR to policy positions outside the scope of the group’s aims and objectives are not appropriate unless the Secretariat has approved it
• Announcing support or funding for publications or events should be approved by the APPGAR Secretariat.
• APPGAR policy positions are agreed by the officers and Parliamentarians of the group. Sponsors, supporting organisations and partners should consider posting social media comments that complement the work and views of the APPGAR.
• APPGAR Advisory Panel meetings are internal meetings so discretion is needed on what constitutes appropriate promotion by sponsors and partners and should be approved by the APPGAR Secretariat.
[1] Kris Manjapra, ‘When will Britain face up to its crimes against humanity,’ The Guardian, 29 March 2018,https://www.theguardian.com/news/2018/mar/29/slavery-abolition-compensation-when-will-britain-face-up-to-its-crimes-against-humanity.
[2] ‘H.R. 3745 Commission to Study Reparation Proposal for African Americans Act,’ 101st Congress (1989–1990), 20 November 1989, https://www.congress.gov/bill/101st-congress/house-bill/3745. Having been submitted by congressman John Conyers Jr every year since 1989, the House Judiciary Committee held a hearing to consider reparations for the descendants of African Americans who had been enslaved on 19 June 2019.
Yesterday, 4th February 2021, the Greater London Assembly (GLA) unanimously passed a motion pertaining to the United Nations International Decade for People of African Descent (IDPAD) moved by Assembly member for the North East London constituency of Hackney, Islington and Waltham Forest, Jennette Arnold OBE, a Labour Co-op Politician.
This press release contains the full text of the motion as follows:
“This Assembly is committed to eradicating and ending racial injustice and anti-Black racism. In our pursuit of these aims, the London Assembly is passing this motion to recognise formally and mark the United Nations International Decade for peoples of African Descent running from 2015-2024.
This Assembly recognises the work undertaken by the Mayor of London in promoting diversity and inclusion, and celebrating Black Londoners through Black History Month activities, the Commission for Diversity in the Public Realm, and working with the Black Curriculum to provide relevant education resources and to review the London Curriculum.
This Assembly calls on the Mayor of London to recognise formally and mark the UN’s Decade by embedding in policies where possible, the UN’s General Assembly resolution on the International Decade for People of African Descent. The Mayor’s work should reflect the following requests from the Programme of Activities for the Implementation of the International Decade for People of African Descent:
Assembly member for Ealing and Hillingdon, Dr Sahota seconded the motion.
London Assembly member Caroline Russell, one of two Green Party representatives on the Assembly and a councillor for Highbury East within the Islington North constituency moved an amendment to the above motion which included the following text:
“The Assembly also notes that the UN International Decade for People of African Descent2015-2024 calls on those that have not yet expressed remorse or presented apologies to find some way to contribute to the restoration of the dignity of victims, and therefore asks the Mayor to support calls for the establishment of an All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth and Reparatory Justice.”
The amendment was also seconded by Green Party London Assembly member Sian Berry, the only Green Party councillor on Camden Council, representing Highgate
See below for the recording of the debate about the motion:
See the full plenary session here: Plenary meeting – YouTube
The full text of Caroline Russell’s speech is as follows:
Thank you chair.
I am so glad that Assembly Member Arnold has brought this motion – it is something we discussed last summer so I am pleased to hear it today.
However, I am proposing an amendment, not to detract from this motion or water down its aims – but to make it more inclusive of the asks of campaigners – and those are the voices I am bringing to the Assembly today.
This motion recognises the UN’s International Decade for Peoples of African Descent and asks that the Mayor’s work reflects some of the actions listed in the Decade – it rightly highlights celebrating Black history, improving education, and anti-discrimination policies.
However, we on the Green Group believe there is a serious omission in this motion and that is the issue of reparatory justice.
The UN International Decade for People of African Descent also has under the programme of activities for the justice theme the text:
“Inviting the international community and its members to honour the memory of the victims of these tragedies with a view to closing those dark chapters in history and as a means of reconciliation and healing; further noting that some have taken the initiative of regretting or expressing remorse or presenting apologies, and calling on all those that have not yet contributed to restoring the dignity of the victims to find appropriate ways to do so and, to this end, appreciating those countries that have done so.”
In London we owe so much to Africans and People of African descent – and not just here in this city, but in all our connections and communities all over the world.
Let me remind everyone listening here today that it was only in 2015 that our Government stopped paying off the debt they took on to “compensate” businesses and people “forced” to stop trading in human lives.
And over the last 200 years the equivalent of £17 billion pounds in today’s money has been paid out.
This so-called “compensation” went the wrong way.
I spoke with the Stop the Maangamizi campaign just yesterday, a group co-led by the extraordinary legal expert Esther Stanford-Xosei and Kofi Mawuli Klu.
She told me that the first thing her campaign group is asking for is to be heard.
For us to hear about the impact of intergeneration harm, for us to hear about what communities are doing to prevent this harm, and for us to hear about how they are healing from this harm.
She asked me to tell you that real reparations mean not just addressing historical enslavement and the money made in human suffering,
But real reparations means recognizing the critical future role that communities and individuals who continue to suffer have to play.
It is vital that communities from the African diaspora are at the heart of the process of any investigation into reparations. Their voices, their stories, their solutions, should be the driving force.
But even working out how to do that starts with establishing a commission to study the impact and legacy of our country’s involvement in slavery and what reparatory justice means.
This is why the amendment I have brought to you today calls on the Mayor to support the establishment of an All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth & Reparatory Justice.
I hope you will vote for this amendment.
Despite the amendment adding teeth to the motion, it fell because only the two Green Party members voted for it. There was value however in raising the arguments and challenging Assembly members to go further than they were clearly prepared to in responding to a global unifying clarion call of Afrikan Heritage Communities to implement their right to remedies and reparations. Nevertheless, this struggle continues unabated!
The GLA motion, which passed unanimously, did not reference or focus on the following key aspects of the IDPAD Programme of action under the justice theme pertaining to reparatory justice:
Stop the Maangamizi Campaign Briefing Note On UK Government Response to Written Question on the All Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth & Reparatory Justice (APPCITARJ) Asked by Baroness Bennett of Manor Castle, Green Party Life Peer [1]
This briefing, which has been shared with members of the Green Party, is our Stop the Maangamizi Campaign position informed by the ‘Law Repairs’ perspective of reparatory justice pertaining to the Law as Resistance strategy we utilise in our critical legal praxis. This comes from the school of jurisprudence to which our critical legal scholar-activists of the International Social Movement for Afrikan Reparations (ISMAR) belong and is also informed by a social movement-lawyering approach.
One definition of movement lawyering put forward by University of California legal expert Betty Hung is a practice which “supports and advances social movements as the building and exercise of collective power, led by the most directly impacted, to achieve systemic, institutional and cultural change”.[2] Movement lawyers maintain a sustained commitment to social movement goals and collaborate with mobilised social movement groups and organizations over time to achieve them; in ways which support grassroots organising and help build the power of the people to bring about forms of redress and solutions to the issues and challenges they face.
The SMWeCGEC was consulted on the following question pertaining to the establishment of the APPCITARJ asked by Baroness Bennett (Green Party) in the House of Lords.
United Nations: Peace Keeping Operations – Question for Foreign, Commonwealth and Development Office, UIN HL10267, tabled on 12 November 2020
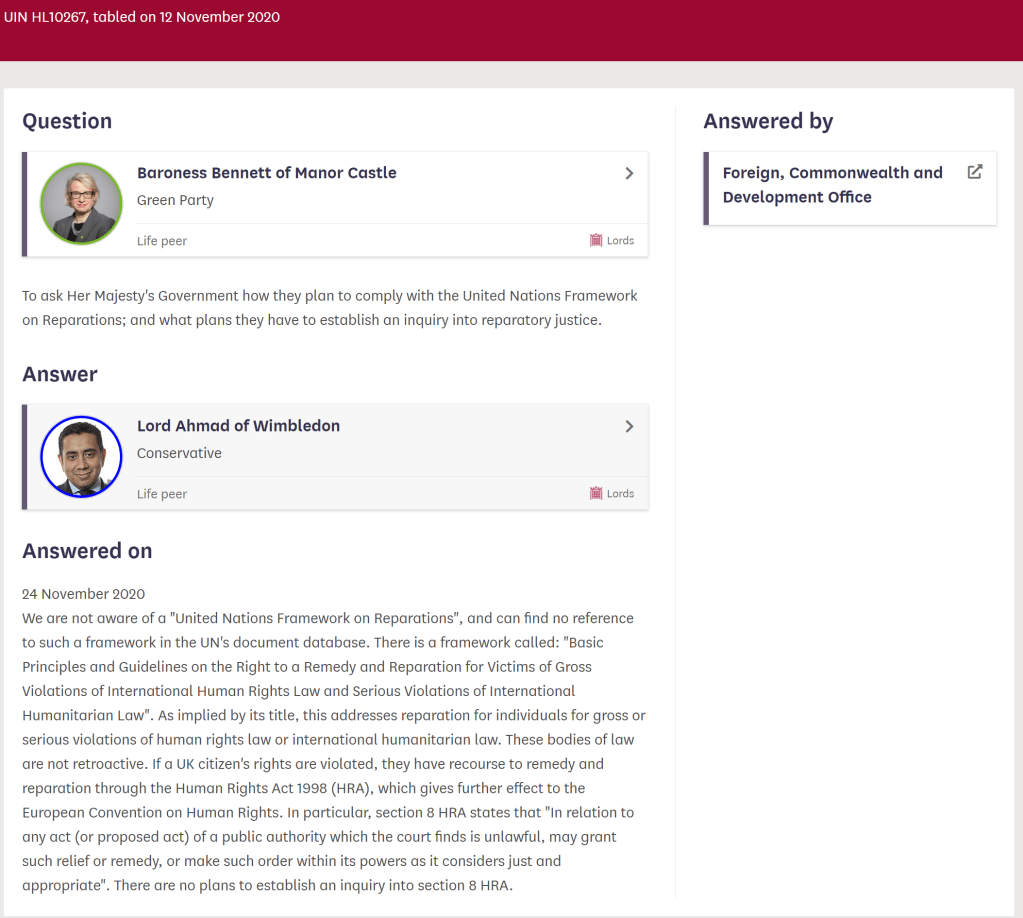
Re: Response from Lord Ahmad of Wimbledon
The ‘Basic Principles and Guidelines on the Right to a Remedy and Reparation for Victims of Gross Violations of International Human Rights Law and Serious Violations of International Humanitarian Law’[3] (hereafter referred to as the Basic Principles) has alternatively been referred to as the UN Framework on Reparations in Green Party documentation. The Basic Principles encapsulate international best-practice standards on reparations at domestic and regional levels. Both international humanitarian law and human rights law are the product of treaties and customary international law, as well as of general principles of law – all of which are sources of international law.
The preamble to The Basic Principles state:
Emphasizing that the Basic Principles and Guidelines contained herein do not entail new international or domestic legal obligations but identify mechanisms, modalities, procedures and methods for the implementation of existing legal obligations under international human rights law and international humanitarian law which are complementary though different as to their norms.
It is the view of the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign that Afrikan Heritage Communities have been and continue to be victimised by the legacies of Afrikan enslavement, colonisation and neocolonialism and recognise the position of Human Rights Watch (HRW) in its ‘Approach To Reparations’ (2001) that:
…The descendants of a victim of human rights abuse should also be able to pursue claims of reparations. That is, the right to reparations should not be extinguished with the death of the victim but can be pursued by his or her heirs.”
Accordingly, the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign has developed its campaign for accountability cognisant of the HRW Position:
For these practical reasons, when addressing relatively old wrongs, we would not base claims of reparations on the past abuse itself but on its contemporary effects. That is, we would focus on people who can reasonably claim that today they personally suffer the effects of past human rights violations through continuing economic or social deprivation.
HRW go on to state:
A group’s ability to identify a wrong to its ancestors would not in itself be enough to claim reparations (although under traditional human rights law its members could pursue claims for abuses against themselves). The group would also have to show continuing harm to itself from those past abuses. This focus on contemporary effects, in our view, provides a firmer and more appealing moral footing for discussions about reparations for old abuses…this approach concentrates on those people who continue to be victimized by past wrongs and seeks to end their victimization.
Re: Lord Ahmad’s statement:
As implied by its title, this addresses reparation for individuals for gross or serious violations of human rights law or international humanitarian law.
The preamble to the Basic Principles also state:
Noting that contemporary forms of victimization, while essentially directed against persons, may nevertheless also be directed against groups of persons who are targeted collectively.
Art. 8 of The Basic Principles state:
Victims are persons who individually or collectively suffered harm, including physical or mental injury, emotional suffering, economic loss or substantial impairment of their fundamental rights, through acts or omissions that constitute gross violations of international human rights law, or serious violations of international humanitarian law. Where appropriate, and in accordance with domestic law, the term “victim” also includes the immediate family or dependants of the direct victim and persons who have suffered harm in intervening to assist victims in distress or to prevent victimization.
The Basic Principles therefore relate to individual and collective victims in that the notion of ‘victim’ includes individual (direct and indirect victims), their families and communities.
Whilst a significant amount of international human rights bodies have utilised reparations jurisprudence pertaining to victimisation directed at individuals, it is also recognised that victimisation may be directed against groups of persons who are targeted collectively and therefore have the right to seek collective redress. Moreover, International law recognises the rights of individuals to exercise certain rights in community with others.
A different concept from that of rights of ‘groups as collective entities’ are the rights of ‘groups of individuals’, such as in the case of international treaties and declarations concerning ‘minorities’. Art. 3(1) of the Declaration on the Rights of Persons Belonging to National or Ethnic, Religious and Linguistic Minorities [4] states that: “Persons belonging to minorities may exercise their rights, including those set forth in the present Declaration, individually as well as in community with other members of their group, without any discrimination”.
Similarly, Art. 3(2) of the European Framework Convention for the Protection of Minorities [5] states: “Persons belonging to national minorities may exercise the rights and enjoy the freedoms flowing from the principles enshrined in the present framework Convention individually as well as in community with others”. Finally, Art. 27 of the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights speaks of the right of persons belonging to minorities to exercise their rights “in community with the other members of their group”.[6]
The dangers posed by the weaknesses of absolutizing the understanding of victims as merely individuals are raised in the following observations in the Practitioners Guide for ‘The Right to a Remedy and Reparation for Gross Human Rights Violations’:
However, it should be clarified that not all international or regional human rights systems have exactly equivalent definitions of the term victim of human rights violations and persons entitled to reparation. Indeed, in some cases, while a person is not considered a victim, he or she may nevertheless have suffered harm and be entitled to reparation. Also, persons who have suffered harm may be considered victims in one system while not in another, but be entitled to reparation in both. In other words: the notion of victim may be narrower than the notion of persons entitled to reparation. This is reflected in Article 41 ECHR and Article 63 ACHR, which, for the purpose of reparation, do not speak of ‘victims’ with regard to this particular obligation of reparation, but of ‘injured party’. The differentiation is not reflected in Principle 8 of the UN Principles on Reparation, which defines victims from the perspective of those entitled to reparation, thus adopting a wide definition of the term victim.[7]
On Retroactivity
Re: Lord Ahmad’s Statement:
These bodies of law are not retroactive.
Art. 6 & 7 of the Basic Principles state:
IV. Statutes of limitations
6. Where so provided for in an applicable treaty or contained in other international legal obligations, statutes of limitations shall not apply to gross violations of international human rights law and serious violations of international humanitarian law which constitute crimes under international law.
7. Domestic statutes of limitations for other types of violations that do not constitute crimes under international law, including those time limitations applicable to civil claims and other procedures, should not be unduly restrictive.
The basis for the demand of the International Social Movement for Afrikan Reparations (ISMAR) for the establishment of the All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth & Reparatory Justice (APPCITARJ) [8] is because of crimes recognised under the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court (which the UK Government signed on 30 November 1998); [9] such as the crime of genocide and crimes against humanity as articulated by the Stop the Maangamizi: We Charge Genocide/Ecocide! Campaign and its petition.[10]
Morally speaking, one cannot impose a statute of limitations on a claim for reparations when the British Government has impaired the ability of victimised Afrikan Heritage Communities to pursue a claim or when the said government continues to deny the claims and rights of Afrikan Heritage Communities to reparations. In this regard, the response received in 2018 by the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign [11] from Lord Ahmad, on behalf of the British Government (“We do not believe reparations are the answer”) is instructive here.
The fact of the matter is, irrespective of the intention of those framing international laws such as the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court and negotiating UN agreements such as the Basic Principles, it is the right of all groups and communities to self-determinedly apply law in their own interests, in consonance with the best interests of all humanity.
The breaking of treaties and other agreements made by colonising authorities in various ways with Indigenous communities which trample upon the rights of these communities and violate law, order and justice as designed for themselves in exercise of their sovereign right to self-determination, must also be given recognition. Such long overdue recognition, in the light of cognitive justice, demands acceptance as legitimate parts of international law in all its forms, the self-designed systems of law, order and justice of Indigenous communities; meaning communities that have suffered colonisation and still have various forms of neocolonialism subjugating them, at present, to settler occupation, robbery of sovereignty and denial of their independent peoplehood. This is what we in the ISMAR regard as the ‘Law Repairs’ of holistic reparatory justice.
On Gross and Serious Violations
According to the Practitioners Guide for ‘The Right to a Remedy and Reparation for Gross Human Rights Violations’:
The Basic Principles do not define either ‘gross violations of international human rights law’ or ‘serious violations of international humanitarian law’. Although not formally defined in international law, ‘gross violations’ and ‘serious violations’ denote types of violations that affect, in qualitative and quantitative terms, the most basic rights of human beings, notably the right to life and the right to physical and moral integrity of the human person. It is generally assumed that genocide, slavery and slave trade, murder, enforced disappearances, torture or other cruel, inhuman or degrading treatment or punishment, prolonged arbitrary detention, deportation or forcible transfer of population, and systematic racial discrimination fall into this category. Deliberate and systematic deprivation of essential foodstuffs, essential primary health care or basic shelter and housing may also amount to gross violations of human rights. In international humanitarian law, ‘serious violations’ are to be distinguished from ‘grave breaches’. The latter refers to atrocious violations that are defined in international humanitarian law but only relating to international armed conflicts. The term ‘serious violations’ is referred to but not defined in international humanitarian law. It denotes severe violations that constitute crimes under international law, whether committed in international or non-international armed conflict. The acts and elements of ‘serious violations’ (along with ‘grave breaches’) are reflected in article 8 of the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court under ‘war crimes’.[12]
It is also important to highlight the fact that these crimes against humanity, including crimes of genocide and ecocide, committed by state and corporate bodies of European imperialism were recognised as crimes not only by Afrikan people but also by peoples of conscience within European countries and their overseas settler colonial communities. In addition, these crimes were resisted. Such resistance resulted in mass movements, like the abolitionist and anti-colonial movements in Europe and other parts of the Global North in solidarity with and involving Indigenous and other communities of resistance throughout the world. That is why it is incorrect to say that such crimes against humanity represented the national will of peoples in Europe. It is noteworthy that this national will reflecting the conscience of the majority in these countries often denounced the genocide and ecocide crimes of the minority ruling classes who abused state power to perpetrate such crimes that stained the national honour of these countries as dissenting voices in these societies have always pointed out.
On the Human Rights Act
Re: Lord Ahmad’s Statement:
If a UK citizen’s rights are violated, they have recourse to remedy and reparation through the Human Rights Act 1998 (HRA), which gives further effect to the European Convention on Human Rights. In particular, section 8 HRA states that “In relation to any act (or proposed act) of a public authority which the court finds is unlawful, may grant such relief or remedy, or make such order within its powers as it considers just and appropriate”. There are no plans to establish an inquiry into section 8 HRA.
The Human Rights Act 1998 aims to “bring rights home”, so that Convention rights can be enforced in the UK courts rather than having to go to Strasbourg. However, narrow interpretations of the Human Rights Act which are in contravention of the letter and spirit of the Act itself, must not be used to defend the indefensible. What is being requested is for the establishment of the All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth & Reparatory Justice (APPCITARJ), not an inquiry into section 8 of the HRA.
The Stop the Maangamizi Campaign has done some thinking and undertaken consultations on what the terms of reference for the APPCITARJ could be; these are included in the ‘Backgrounder About The All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth & Reparatory Justice’.[13]

The Stop the Maangamizi Petition reiterates the point that the demand for the APPCITARJ is necessary “to advance the process of dialogue from the ground-upwards, with the British State and society on Reparatory Justice”.
Art. 11 of the Basic Principles explains:
Remedies for gross violations of international human rights law and serious violations of international humanitarian law include the victim’s right to the following as provided for under international law:
(a) Equal and effective access to justice;
(b) Adequate, effective and prompt reparation for harm suffered;
(c) Access to relevant information concerning violations and reparation mechanisms.
The European Court has held that the failure to conduct an effective investigation into credible allegations of human rights violations may violate the right to an effective remedy of the victim and/or their relatives.[14]
Suggested Follow-Up Question
From this briefing we in the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign suggest Baroness Natalie Bennett can pose a follow-up question along the following lines:
To ask Her Majesty’s Government, will it now, in connection with the International Decade for People of African Descent, recognise the importance of an inquiry into reparatory justice for tackling the legacies of Afrikan Enslavement such as Afriphobia, colonisation and neocolonialism, with holistic measures, including redressing the climate and ecological crises in ways that ensures that the voices of Afrikans and their descendants are properly heard and Planet Repairs delivers global justice to all.
Esther Stanford-Xosei, Coordinator General, Stop The Maangamizi: We Charge Genocide Ecocide Campaign (SMWeCGEC)
30/11/20
There are two ways of seeing and interpreting international legal transformation – from above as most lawyers do when they focus on formal sources, judicial opinions, and treaties exclusively – or from below when we focus on the lived experience of ordinary people with international law when they encounter international institutions, frame their demands in international legal terms, and network for influencing international or domestic policy.
Balakrishnan Rajagopal, International Law From Below, 2005
[1] https://questions-statements.parliament.uk/written-questions/detail/2020-11-12/hl10267
[2] Movement Lawyering as Rebellious Lawyering by Betty Hung
https://www.law.nyu.edu/sites/default/files/upload_documents/Betty%20Hung%20–%20Movement%20Lawyering.pdf
[3] https://www.ohchr.org/en/professionalinterest/pages/remedyandreparation.aspx
[4] https://www.ohchr.org/en/professionalinterest/pages/minorities.aspx
[5] https://www.coe.int/en/web/conventions/full-list/-/conventions/rms/090000168007cdac
[6] https://www.ohchr.org/en/professionalinterest/pages/ccpr.aspx
[7] Universal-Right-to-a-Remedy-Publications-Reports-Practitioners-Guides-2018-ENG.pdf (icj.org)
[9] https://www.legislation.gov.uk/ukpga/2001/17/contents
[10] https://www.change.org/p/stop-the-maangamizi-we-charge-genocide-ecocide
[14] Aksoy v Turkey, ECtHR, Judgment of 18 December 1996, Reports 1996-VII,paras 95-100.


This article is based on that of Green Party member Dr Nicola Frith in Green world on 19/10/20 published here.
In a historic move, the Green Party of England and Wales has become the first major national party to commit to seeking reparatory justice for the transatlantic trafficking of enslaved Afrikans (TTEA).
Members overwhelmingly voted in favour of the E3 motion ‘Atonement and Reparative Justice For African Enslavement‘ on the final day of their Autumn Conference on the 11th October 2020. Proposed by Green Councillors Cleo Lake (Bristol) and Scott Ainslie (Lambeth), and supported by the Greens of Colour and the Young Greens, the motion will see the Green Party call on Parliament to establish an All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth and Reparatory Justice.
Azzees Minott, chair of the Greens of Colour and a significant contributor to getting the motion adopted, stated, ‘I am thrilled that Greens have been able to lead a historic movement in Britain by passing this motion. So many people see the Greens as a single-issue party, but achieving true social and racial justice is also at the core of what members care about because it’s all connected.’
Tyrone Scott from the Young Greens added: ‘As a young person of African descent, it has always been a source of shame to me that the UK was so complicit in enslavement. Our school curriculum only offers the most basic teachings of our colonial past, which generally only celebrates the power of the British Empire without detailing how this created deep racial inequalities in this country and across the world, which continue to exist to this day. The Young Greens were proud to work on this groundbreaking motion which sets a precedent to all other UK political parties.’
The All-Party Commission of Inquiry for Truth and Reparatory Justice is a campaigning project founded by the Pan-Afrikan Reparations Coalition in Europe (PARCOE) and now driven by the Stop the Maangamizi: We Charge Genocide/Ecocide Campaign (SMWeCGEC).
The need for this Commission has long been supported by the work and activism of other members of the International Social Movement for Afrikan Reparations (ISMAR), including those of the Pan-Afrikan Liberation Movement, the Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations March Committee and the International Network of Scholars and Activists for Afrikan Reparations (INOSAAR).
The campaign aims to urge the UK Government to commit to a holistic process of atonement and reparations in accordance with the United Nations Framework on a Right to a Remedy and Reparation. A key part of the process includes recognizing and addressing the longstanding legacies of slavery, colonialism and neo-colonialism, such as the racial discrimination of majority world peoples, socio-economic inequality and environmental injustice.
Cleo Lake said, ‘Getting this motion to conference has been a great example of collaborative working with key reparations campaigners.
‘It represents a significant milestone towards acknowledgement, justice and reconciliation over a painful shared history, the legacy of which still plays out today through rife global inequality, racism, Afriphobia, and a ravaged planet that continues to be pillaged and disrespected.’
The vote at national level follows on from the work of Lambeth Council, led by Green Party Councillor, Scott Ainslie. Earlier this year, Lambeth, which is home to the largest African-Caribbean population in the UK, became the first local authority to pass a successful motion calling for an All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth and Reparatory Justice to address the impact of slavery on current racial inequalities in the UK.
Ainslie, who co-signed the motion to Conference, said: ‘This motion is a step towards “Global Britain” finally facing up to the impact it has on countries throughout the world.
‘If Britain can properly address the legacies of its colonial past and present, then it can truly deal with the root causes of our country’s socio-economic inequality and systemic racism.
‘By engaging in a genuine process of reparative and transitional justice, we can begin to heal holistically and re-balance these injustices inflicted by the few which cause endless suffering to the many.’
At the root of this motion lies the work of some of the UK’s foremost reparations scholar-activists: Esther Stanford-Xosei and Kofi Mawuli Klu, co-vice chairs of the Pan-Afrikan Reparations Coalition in Europe (PARCOE).
Since 2001, PARCOE has been leading different reparative initiatives, including the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign and its petition, which has gained over 20,000 paper and online signatures. PARCOE have long been working to put the voices of grassroots and Afrikan Heritage Communities at the centre of the struggle for reparations.
Klu described the motion as a ‘giant leap’ for Afrikan Heritage Communities of reparations interest as they march towards ‘self-determination to achieve reparations that will meaningfully impact on Planet Repairs.’
He paid tribute to others in the ISMAR and the Peoples Reparations International Movement (PRIM), noting that ‘with this enlarging grassroots force of peoples becoming the change, we can now convincingly express confidence in our ability to win the case for the All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth and Reparatory Justice and make reparations doable as a unifying force of all who desire Planet Repairs.’
He noted that it has taken ‘almost three decades of painstaking campaigning endeavours to raise consciousness enough for such results to be the works of not just a few, but the many, including now the Greens of Colour and Young Greens.’
Esther Stanford-Xosei, Coordinator-General of the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign, said, ‘The passing of this motion by the Green Party is vindication of our efforts. We have believed all along that our community organising efforts will eventually have the ground-up impact of winning more allies who grasp the necessity for an All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth and Reparatory Justice and understand it as a repairing process.’
‘This repair is important, not only for the restoration of the agency of our Afrikan Heritage Communities and stopping the despoliation of the Earth as our human habitat, but also for the rebalancing of society. Afrikan Reparations is a cause that will redress the globalised historical and contemporary injustices of what we call the Maangamizi (Afrikan Holocaust of chattel, colonial and neo-colonial enslavement).’
Emphasising the unifying narrative of reparations and its integral links to environmentalism, she stated that ‘no home in the world has been untouched by such manifestations of the Maangamizi as the climate and ecological crises.
‘That is why the Afrikan reparations we are seeking must have the Planet Repairs impact of restoring the familyhood of humanity which began from our Afrikan peopling of the entire world.’
Passing the motion at national level is, however, only the first step. The next step is to build on existing work that is underway between communities and councillors at local levels.
As Lake states, ‘The aim is that as many local authorities as possible also pass motions calling for the All-Party Commission, as well as other overarching and region specific resolutions.’
Cities with direct links to the transoceanic trafficking in enslaved Afrikans and areas with strong Green support will be selected as priorities.
To improve understanding about reparations as a holistic process and its links to Planet Repairs, Greens of Colour will be working with the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign and the INOSAAR to produce motion templates and guidance, as well as dedicated workshops for councillors, regional parties, activists and citizens. In the meantime, further information and FAQs can be found on the Green Party Living Room.
Esther Stanford-Xosei and Kofi Mawuli Klu participated in a Green Party conference fringe session with Cllrs Scott Ainslie and Cleo Lake organised by Greens of Colour to sensitise Green Party members to the contents of the motion on 3rd October 2020. The recording of the session can be found here.

This is an edited version of the statement provided to, Beth Ani, a journalist with the Morning Star Newspaper, in response to a request made on Sunday 2nd August 2020
I am a journalist at the Morning Star newspaper – i’m wondering if you could send a comment on yesterday’s march and also respond to Nigel Farage’s comments in which he described scenes at the protest as “terrifying” and accused BLM of “diving society.” Let me know if you’re able to comment, many thanks, Beth.
This is the Morning Star article were some of the above comments were included.
As to Nigel Farage’s completely unjustified comments: “Terrifying scenes in Brixton today. A paramilitary-style force marching in the streets. This is what the BLM movement wanted from the start and it will divide our society like never before”, they should be taken for the racist nonsense and deceitful propaganda that they are. Farage’s comments were an abysmal attempt to frighten away allies from supporting these Reparations Rebellion Groundings of our Afrikan Heritage Communities; and connecting their own actions of rebellion to ours. Far from dividing society, this year’s Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations Rebellion Groundings became a cross-community unifying celebration of the internationalist solidarity, and its best traditions, that have always brought together peoples from diverse communities of resistance, within and outside of the UK, to strengthen their cooperation in fighting to eradicate the divisive weapon of racism.
We deliberately organised this year’s Afrikan Emancipation Day activities in ways to counter the use of racism, by the elitist establishment of Global Apartheid racism, to keep all communities of resistance apart from each other, and therefore make it difficult for us to collectively achieve the desired victory of total emancipation for all Humanity to reclaim the Planet and build a multipolar World of Global Justice for All. The deceptive fear mongering of the white supremacy racist ilk of Nigel Farage is not going to stop us progressing this work of rebuilding principled unity in continuation of similar efforts in the past.

Learning from our predecessors, (whose efforts in this same direction were given recognition in the British champions of internationalist solidarity section of our Sankofasafarinta Exhibition at Max Roach Park), as part of the Reparations Rebellion Groundings, we are better prepared now to defend this work of forging principled unity as a necessity for advancing all of us towards the Rendezvous of Victory that our own Pan-Afrikan freedom-fighters like Aimé Césaire long ago envisioned for us. This is what we mean by our slogan ‘Stop the Maangamizi: Build Maatubuntuman in Ubuntudunia!’
Esther Stanford-Xosei, Coordinator General, Stop the Maangamizi: We Charge Genocide/Ecocide Campaign


Although our plan could not be fully executed because of unfair UK Government and police impositions, our overall assessment is that of success in the fact that most of what we had planned was carried out.

Support Received
We received extensive support from diverse sections of our Afrikan Heritage Communities, including many supporting and contributing community based organisations, who came out in their thousands, (not hundreds as many of the media reports are mis-reporting). We take pride in the fact that despite fearmongering and threats from the police and the entire British State machinery, our people still came out defiantly in support of our call to unity for Reparatory Justice action.
We acknowledge the fact that, because of the government and state anti-terrorism policing impositions imposed within less than 24 hours of our Reparations Rebellion Groundings, a few shortcomings made what we had planned as co-organisers not to be fully realised. Such short-comings, some of which were due to interferences and obstructions from central government were taken advantage of, by the British state machinery, to falsify and create situations of make-believe conflict that resulted in 3 arrests and threatened to provoke our Black communities in attendance, into what could have degenerated into rioting.

We have good cause to say so because on the morning of the 1st of August, a member of the public who was driving in his car in the vicinity of where the Reparations Rebellion Groundings were meant to be taking place, observed police officers piling bricks into a police van. The member of the public described the bricks as being “proper house bricks” so Leo Muhammad, a longstanding member of the Nation of Islam, but who was not working in an official capacity, but rather participated in the Reparations Rebellion Groundings as a longstanding member of the Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations March Committee, reported this incident to Superintendent Ian Howell (Lambeth Borough), Police Liaison Officer Sergeant Simon Hearn and Community Liaison Officer, Lance Edmondson, based at Brixton Police Station. Leo Muhammad was accompanied by the eye-witness and a security officer supporting our security and stewarding operations for the Reparations Rebellion Groundings, who was wearing a body camera and therefore such reporting of this incident was recorded.
As co-organisers, we in the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign and Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations March Committee up till now have not received a satisfactory answer to the request to know why police officers were seen piling bricks into a police van. The explanation provided was that the local authorities, Lambeth Council had been doing some “cleaning up”. Notwithstanding the aforementioned, as co-organisers, we would like to express our appreciation to Extinction Rebellion Police Liaison, Paul Stephens who brilliantly helped us in working reasonably well with the police in general but also particularly with Police Liaison Officer Sergeant Simon Hearn and Community Liaison Officer, Lance Edmondson who genuinely tried to help and facilitate us to ensure that the Reparations Rebellion Groundings ran peacefully according to our purpose.
Through the increasing level of awareness and collective discipline that we are cultivating in our Afrikan Heritage Communities and in the building of cross-community alliances and ‘movement of movements’ cooperative relationships, such provocations, were pre-empted and resisted from our peaceful standpoint of non-violent direct action. We are grateful to our own Afrikan Heritage Communities and all who came in solidarity for enabling us to defeat the shenanigans and machinations of the British state machinery and other white supremacy racist agent provocateurs so that our activities on the day were held successfully in accordance with our ancestral Afrikan visions, values and principles of Ma’at and Ubuntu to ensure a peaceful success in tune with our Reparatory Justice demands for Planet Repairs.
We are appreciative of our youth and student contingents from the Tribe Named Athari (TNA) and Rhodes Must Fall Oxford (RMFO) who contributed immensely to ensuring that the participation of the younger generation manifested the ethos of our Afrikan Emancipation Day commemorations as those of Reparations Rebellion Groundings in their real community educational meaning promoted by Dr Walter Rodney. We express our highest regards to various allies particularly those from Extinction Rebellion (XR) who demonstrated some of the best traditions of internationalist solidarity long displayed by progressive forces in Britain by acting in strict accordance with roles we had agreed that they would play, in contributing to the success of our activities on the day, through the facilitation of the Extinction Rebellion Internationalist Solidarity Network (XRISN).
We also express our gratitude to Councillors like Cllr. Scott Ainslie, and Cllr. Cleo Lake, who have been leading our engagement with the Green Party in getting ‘Atonement and Reparations’ motions passed by Lambeth Council on 15th July 2020 and Islington Council on the 9th July 2020. We particularly commend those in Lambeth Council whose version of the motion passed highlighted our need for the UK Government to establish the All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth & Reparatory Justice (APPCITARJ). The APPCITARJ is what we, as co-organisers from the International Social Movement for Afrikan Reparations see as the essential starting point for British state action in facilitating the masses of our Afrikan Heritage Communities across the World to access just hearings; which is in itself a reparative measure in accordance with the UN Framework on a Right to a Remedy and Reparations.
We are encouraged by the growing support from our Afrikan Heritage and other Black Communities, as well as wider sections of society in Britain, including diverse communities of the Global South Diasporas. We are glad that many in these communities are increasingly recognising the need for all of us to build the kind of principled unity that will enable the prolonging resistance efforts of our communities in the Global South to merge into the Global Rebellion that will deliver victory to all of us in ways that will not only make us win our specific community Reparations goals but also ensure the achievement of all the necessary Planet Repairs. For it is such holistic repairs to Peoples and Planet that will guarantee a cessation of violations and non-repetition of what we refer to as the Maangamizi (Afrikan Hellacaust), so that we shall have a New World of enduring Global Justice for all.
The Way Forward
We shall continue to work in advancing the momentum reinvigorated by the 1st Mosiah (August ) Afrikan and support the likes of A Tribe Named Athari (TNA) and allies who are working to earn for themselves places of honour in the front-ranks of the International Social Movement Afrikan Reparations (ISMAR) and the Peoples Reparations International Movement (PRIM) respectively.

We encourage community members, supporters and allies to do any of the following 4 things:
 This is a link to an article we have on our website, with a template Stop The Maangamizi Postcard and template letter which can be amended from the perspective of allies supporting this demand.
This is a link to an article we have on our website, with a template Stop The Maangamizi Postcard and template letter which can be amended from the perspective of allies supporting this demand.In accordance with the Afrikan visionary ethical framework of MA’AT, we are supporting XR, through XRISN, to work towards the successful holding of its next phase of rebellion ‘We want to live – The Rebellion returns to Parliament on 1 September amidst warnings of a 4°C world‘; doing so in ways that will take shared learning from our 1st August Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations Rebellion Groundings into their own manifestations of non-violent direct action – ‘From Brixton Lockdown to Parliament Lockout’. We are planning to organise an interfaith human chain to surround the British Houses of Parliament with ceremonies to exorcise the criminal demons of genocide and ecocide out of such a Maangamizi crime scene to prepare this institution to host the APPCITARJ. Such spiritual cleansing ceremonies will be conducted by Indigenous spiritual practitioners of liberation theology from Afrika and other regions of the Global South assisted by interested people of all faiths in the Global North. By so doing, we shall be strengthening People-to-Peoples Internationalist Solidarity in order to move all progressive forces of Humanity harmoniously towards our common objective of ‘Planet Repairs!’ as expressed in our Reparatory Justice slogan of ‘Stop The Maangamizi – We have Ubuntudunia to Win’.

We are inviting all from our Afrikan Heritage Communities and allies to join us in responding to the internationalist solidarity gesture of the New Tribe and their supporters from the communities of resistance of the South Abya Yalan (so-called Americas) Diaspora, who participated in the edutainment activities of our Reparations Rebellion Groundings in Brixton to support their own forthcoming commemoration of 12th October, as the International Day of Indigenous Resistance. Together, in such actions of true internationalist solidarity, we all shall win.
For us in the Stop the Maangamizi Campaign and others in our ‘coalition of the willing’, preparation for 1st August 2021 Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations Rebellion Groundings start from today, 3rd August 2020. Such Groundings will take place in the same area we were meant to lock-down in Brixton from Windrush Square to Max Roach Park including Brixton Road.
Esther Stanford-Xosei
Coordinator General, Stop The Maangamizi: We Charge Genocide/Ecocide Campaign (SMWeCGEC)
Esther is also the official spokesperson for the Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations March Committee (AEDRMC) and Co-founder of Extinction Rebellion Internationalist Solidarity Network (XRISN)
See our response to Nigel Farage’s disparaging remarks here.

Further to our earlier post yesterday (below), it has come to our attention that the Atonement and Reparations for the United Kingdom’s Transatlantic Traffic in Enslaved Africans motion moved by Islington Green Party Cllr Caroline Russell was amended by Labour Party Cllr Gulcin Ozdemir.
One of the significant amendments was removal of the text:
Write to the Speaker of Parliament, Chair of the Women & Equalities Committee and Chair of the Home Office committee to request that they establish, and seek UK Government support for the establishment of an All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth and Reparatory Justice and calling on the Government to commit to holistic reparations taking into consideration various proposals for reparations in accordance with the United Nations Framework on Reparations.
Unfortunately, the Islington motion moved by Cllr Caroline Russell and also retained in the amended motion by Cllr Gulcin Ozdemir also omitted (we were told by accident due to working with an older draft of which there were several) this key text:
Of course these omissions are unacceptable to us and we await the passing of the Lambeth Council Resolution on 15/07/20.
The full amendments to the Islington text can be found here:
AMENDED ISLINGTON MOTION PAGES 1-6
Please read the following text in light of what we have recently discovered.
Original Post 11/07/20
We are pleased to report to you that the ‘Stop the Maangamzi: We Charge Genocide/Ecocide!’ Campaign (SMWeCGEC) has been part of the drafting of a historic motion on reparations passed by Islington Council on 9th July 2020, (see below). The motion was moved by Green Party Cllr Caroline Russell. This motion came about as a result of SMWeCGEC teamwork with Cllr Scott Ainslie from Lambeth Green Party, other colleagues in the Green Party & Greens of Colour, as well as Cllrs in Lambeth & Islington Labour Party. It builds on the demand in the Stop the Maangamizi postcard calling for elected officials to support the demand for the establishment of the All-Party Parliamentary Commission on Inquiry for Truth & Reparatory Justice (APPCITARJ).

This motion is largely an outcome of engagement with Cllr Scott Ainslie in demonstration of his commitment made at the 2019 Afrikan Emancipation Day Reparations March to follow-up with a motion on reparations. The motion in Islington was able to pass because of Green Party and Labour Party collaboration and consensus-building around key aspects of the text that the SMWeCGEC contributed and which were added to by members of the Green Party and the Labour Party.
From the SMWeCGEC’s perspective, one of the highlights of this Islington Council Reparations Motion is recognition of our campaign demand for the establishment of the APPCITARJ, which is an essential phase in a participatory administrative reparations process. In addition to reference to selected landmarks in the UK chronology of campaigning on reparations. We also contributed significant amounts of text to the original Islington and Lambeth motion.
A similar motion was submitted by Green Party Cllr Cleo Lake in Bristol on 7th July 2020.
The first drafted motion spearheaded by Cllr Ainslie will actually be voted on by Lambeth Council at the forthcoming Council meeting on Wednesday 15th July 2020.
The SMWeCGEC is truly appreciative of Cllr Ainslie and all others that worked with him from the Lambeth Green Party, Greens of Colour, including Cllr Lake and also Cllr Russell, to ensure that such motions could be submitted.
Cllr Scott has truly been exemplary in working in such a way which honours the guidance in the INOSAAR Principles of Participation in recognising the existence of the International Social Movement for Afrikan Reparations (ISMAR); and the necessary ethics that this entails. This includes respecting the existence of historical and contemporary reparations work, research and other initiatives at regional, national and transnational levels.
We are also pleased that engagement with the Green Party which was commenced years earlier (between 2002 – 4) with other Green Party elected officials under the auspices of the then Rendezvous of Victory, has now borne some outcomes that help take the goals of the International Social Movement for Afrikan Reparations (ISMAR) Further.

We also take this opportunity for recognising the efforts of Lucie Scott in Hackney who recently got in touch to inform us that she had proposed a motion passed in 2018 which recognised the demand for the APPCITARJ. See here Hackney NSN 2018 IR motionFinal (1) for further info.
The following are a few relevant tweets and other publicity:
https://twitter.com/bristolgreen/status/1281195994219241472?s=20

Dr #WalterRodney‘s wisdom is relevant to #Afrikan struggle 4 #Reparations “A struggle doesn’t drop from the sky; it has roots, it has been going on for years; people’s energies, their consciousness, their organizations have evolved in response to specific historical conditions.”
The following video featuring Esther Stanford-Xosei, legal advisor to then existing Black Quest For Justice Campaign (BQJC), is one of the earliest video recordings which tracks the demand for what has now become known as the All-Party Parliamentary Commission of Inquiry for Truth & Reparatory Justice (APPCITARJ). However its modern-day antecedents, as well as that of the Ubuntukgotla People’s International Tribunal For Global Justice (U-PITGJ) can be traced back to the the work of Kofi Mawuli Klu who wrote the following paper Charting an African Self-Determined Path of Legal Struggle for Reparations as a contribution to the 11 December 1993 working conference of the African Reparations Movement (ARM UK), co-founded by the late Bernie Grant MP and others.
The following comments from SMWeCGEC Co-Initiator and Co-Vice Chair, Kofi Mawuli Klu provide another layer of historical context to the significance of this motion for the SMWeCGEC and the wider ISMAR.
Also this comment from Kofi is in response to a dialogue between him and Akyaaba Addai-Sedo based in Ghana about the same motion.
Yes, the awesome beauty of this historic action of the London Borough of Islington, to which the work of yourself, Brother Akyaaba and others of the GLC, contributed upon the foundations laid throughout the ages by Kodwo Enu (Ottobah Cuguano), Olaudah Equiano, Frederick Douglas, Henry Sylvester Williams, John Archer, Marcus and Akosua Boahemaa Amy Garvey, CLR James, Claudia Jones, Paul Robeson, George Padmore, Ras Makonnen, WEB DuBois, Osagyefo Kwame Nkrumah and his stalwarts of the Pan-Afrikan Congresses, is the change in Language and concepts insisted upon by our Stop the Maangamizi: We Charge Genocide/Ecocide Campaign (SMWECGEC), backed strongly by our colleagues of the INOSAAR based at the University of Edinburgh, and friends of the Green Party! So, for example, instead of the so-called very derogatory insulting ‘Slave Trade’, which the likes of Walter Rodney had very well repudiated as no trade at all, there is now acceptance of our PARCOE formulation that it is the Transatlantic Trafficking of Enslaved Afrikans (TTEA)!
Not yet Uhuru; but there is now being galvanized by new waves of Rebellion at home and abroad our Long March to the victorious Reparatory Justice achievement of the Pan-Afrikan revolutionary winning of Planet Repairs, in order to secure our own MAATUBUNTUMAN Pan-Afrikan Union of our Communities of Resistance, stronger unifying those in our Mothercontinent with those in the diaspora, in a New Global Justice World of UBUNTUDUNIA, not by opportunistically riding upon the topdown ramshackle bandwagons of Neocolonialism like the so-called African Union (AU) of misleaders, but rather by the independently organised grassroots-embedded Worldwide Black Power of our Afrikan People in our own Afrikan Communities of Resistance!
Forward Ever Onward!
There is Victory for Us!
Amanda Ngawethu!
Elsewhere, Kofi says this:
Thanks, Sister Esther, Yes, our Stretch of the Maangamizi Counteraction Intergenerational Long March of our ancestral Freedomfighting Afrikan Sheroes and Heroes has now come to one of its major decisive Reparatory Justice Turning Points towards our long desired total Pan-Afrikan Liberatory Rendezvous of Planet Repairing Global Justice Victory! Now is Our Time to Seize WISER than ever before to ensure our Pan-Afrikan Reparatory Justice Making of, and Black People’s Power contributions to, the Global Justice Writing of true World Ourstory/History is accelerated to its definitive, irreversible and completely victorious destination! Our MawuLisaga, the almighty God of Afrika and the entire World of, and beyond, Miano Nana Asase Yaa Mother Earth be thanked, with all the gratitude due also to our revered Ancestors, for the day we met to begin battling together for the more systematic movement building harmonization of the collective and individual efforts of our Afrikan people glocally towards the better intellectually organic and organisationally disciplined achievement of this sacred purpose! Akpe: Thank you very much!
The rest of us also agree with Kofi who has rightly stated elsewhere:
The biggest gratitude goes to the God of Afrika and the Pluriverse, to our revered Ancestors and also to all of us who have kept faith with them for a true Reparatory Justice that can only be holistic Planet Repairs in its Global Justice for all meaningfulness! Lots more work to do!
Until next time!
‘Stop the Maangamizi: We Charge Genocide/Ecocide! Campaign International Steering Committee Spearhead Team (ISC-SMWeCGEC)